However, the company is owed $90,000 and will still try to collect the entire $90,000 and not just the $85,200. Bad debt expenses are classified as operating costs, and you can usually find them on your business’ income statement under selling, general & administrative costs (SG&A). This method aligns with the matching principle of GAAP, ensuring that the expense is recognized in the same period as the related revenue.
What is Accounts Receivable Collection Period? (Definition, Formula, and Example)
In order to understand the required journal entries used with the allowance method, assume that during 2019, Delta Corporation’s first year in business, sales totaled $1 million. Assume further that the company’s past history and other relevant information indicate to officials that approximately 7 percent of all credit sales will prove to be uncollectible. An expense of $7,000 (7 percent of $100,000) is anticipated because only $93,000 in cash is expected from these receivables rather than the full $100,000. Notice, other than the amount and description, this is the same entry we made under the percentage of sales method.
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
The bad debt expense account is used to record the estimated uncollectible accounts for the period. The Allowance Method is the preferred approach under GAAP for estimating and accounting for uncollectible accounts. This method involves creating an allowance for doubtful accounts, a contra-asset account that offsets the accounts receivable on the balance sheet. The purpose of the allowance method is to anticipate potential losses from uncollectible accounts and match these estimated losses to the same period in which the related sales occurred. This ensures that the financial statements accurately reflect the true economic condition of the company. As the accountant for a large publicly traded food company, youare considering whether or not you need to change your bad debtestimation method.
Financial Accounting
- This method is labeled a balance sheet approach because the one figure being estimated (the allowance for doubtful accounts) is found on the balance sheet.
- Effective credit policies help in balancing sales growth with the risk of bad debts, ensuring that credit is extended to customers who are likely to pay.
- The companies that qualify for thisexemption, however, are typically small and not major participantsin the credit market.
- This estimation creates an allowance for doubtful accounts, which is a contra-asset account that offsets accounts receivable.
- In either case, bad debt represents a reduction in net income, so in many ways, bad debt has characteristics of both an expense and a loss account.
- This involves debiting or crediting the allowance for doubtful accounts account and the bad debt expense account.
The second method—percentage-of-receivables method—focuses on the balance sheet and the relationship of the allowance for uncollectible accounts to accounts receivable. Continuing our examination of the balance sheet method, assumethat BWW’s end-of-year accounts receivable balance totaled$324,850. This entry assumes a zero balance in Allowance forDoubtful Accounts from the prior period. Carefully consider that the allowance methods all result in the recording of estimated bad debts expense during the same time periods as the related credit sales. Based on this calculation the allowance method estimates that, of the credit sales of 65,000, an amount of 1,625 will become uncollectible at some point in the future.
During the interim, bad debts are estimated and recorded on the income statement as an expense and on the balance sheet through an allowance account, a contra asset. In that way, the receivable balance is shown at net realizable value while expenses are recognized in the same period as the sale to correspond with the matching principle. When financial statements are prepared, an estimation of the uncollectible amounts is made and an adjusting entry recorded.
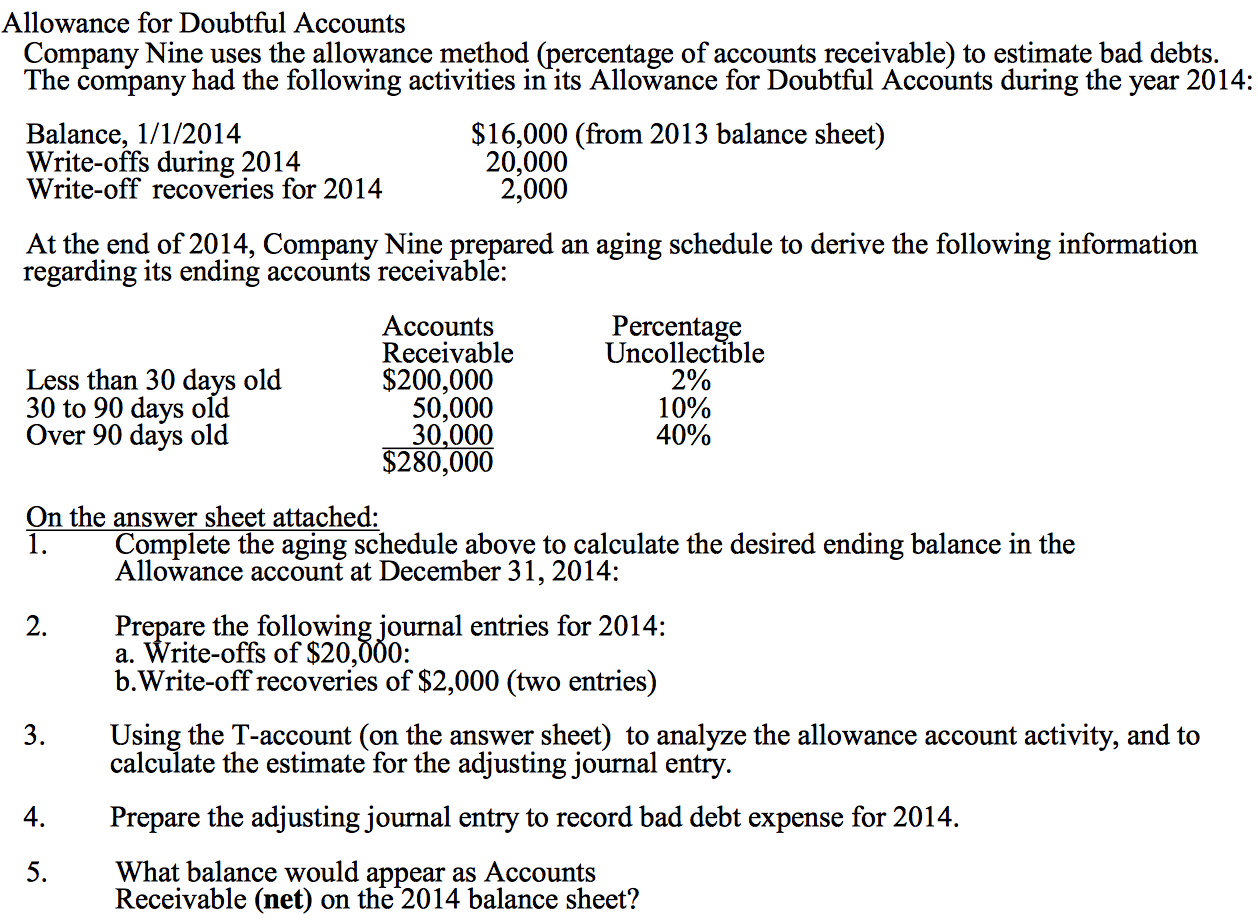
Accounts Receivable Aging Method
Our intuitive software automates the busywork with powerful tools and features designed to help you simplify your financial management and make informed business decisions. Bench simplifies your small business accounting by combining intuitive software that automates the busywork with real, professional human support. This approach allows the reader to calculate the proportion of the total group that is believed to be collectible or uncollectible. Since the entry that recognizes the expense also reduces current assets by an increase in the Allowance for Uncollectibles, it also reduces working capital. If all or part of a previously written off account is actually collected, several procedures are possible. When this information is available, it can be used to predict the uncollectible amount.
The two main methods of estimating Uncollectible Accounts Receivable are the percentage-of-net-sales method and the aging method. The percentage-of-net-sales method is the simpler of the 2021 federal quarterly estimated tax payments two and involves calculating an allowance based on a percentage of net sales. The aging method is more complex and requires analyzing customer accounts to determine their collectibility.

Accurate and reliable financial statements are crucial for building trust with stakeholders, making informed business decisions, and achieving long-term success. As of January 1, 2018, GAAP requires a change in how health-careentities record bad debt expense. Before this change, theseentities would record revenues for billed services, even if theydid not expect to collect any payment from the patient.
As a result, companies need to account for the possibility of uncollectible accounts, which are also known as bad debts. You may notice that all three methods use the same accounts for the adjusting entry; only the method changes the financial outcome. Also note that it is a requirement that the estimation method be disclosed in the notes of financial statements so stakeholders can make informed decisions. If you do a lot of business on credit, you might want to account for your bad debts ahead of time using the allowance method.
The bad debt expense for the accounting period is recorded with the following percentage of accounts receivable method journal entry. The previous allowance method directly estimated the bad debt expense based on the credit sales recorded on the income statement of the business. Uncollectible Accounts Expense, also known as Bad Debt Expense or Doubtful Accounts Expense, is an expense account representing the estimated amount of accounts receivable that a business expects it will not be able to collect. Essentially, it’s an acknowledgment that not all customers who owe money to the company will pay their debts.


Claim Free Play with the 1xBet Free Promo Code
아이디판매
Claim Free Play with the 1xBet Free Promo Code
اجاره خودرو در شیراز
Plinko's Use of Predictive Analytics at Stake UK Casino
UFAAUTO789
Plinko's Use of Predictive Analytics at Stake UK Casino
UFAAUTO789
Claim Free Play with the 1xBet Free Promo Code
this site